In the world of materials science, metallurgy, chemistry, and industrial research, precise heat treatment is essential. One of the most widely used tools for this purpose is the tubular furnace — a specialized high-temperature device designed for uniform heating in laboratory and production environments.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or technician, this guide will give you a clear understanding of what a tubular furnace is, how it works, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What Is a Tubular Furnace?
A tubular furnace is an electric resistance heating device featuring a cylindrical chamber, often constructed from quartz, alumina, or metal, designed to evenly heat materials at elevated temperatures. The heating element surrounds the tube and can raise the temperature to several hundred or even thousands of degrees Celsius, depending on the model.
Tubular furnaces are well-suited for applications including:
- Annealing
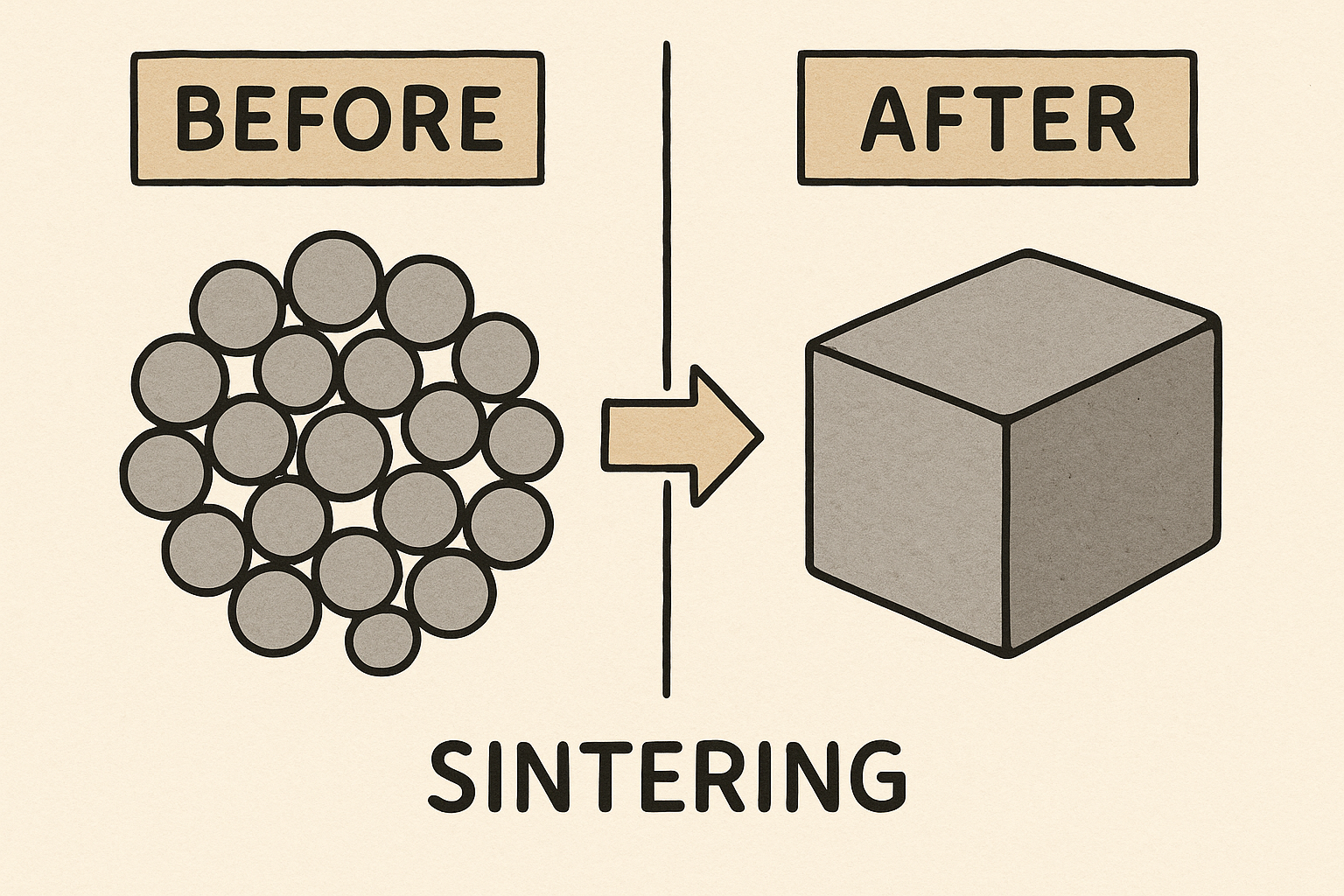
- Sintering
- Pyrolysis
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
- Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Key Features of a Tubular Furnace
High-Temperature Capability
Most high temperature tubular furnaces operate within a range of 300°C to 1800°C, depending on the type of heating element (e.g., Kanthal, MoSi₂, graphite) and insulation used.
Tube Configuration
You can choose between:
- Horizontal tubular furnace: Suitable for longer materials and continuous flow systems.
- Vertical tubular furnace: Ideal for gravity-fed reactions or when precise vertical alignment is required.
Atmosphere Control
Many models allow for inert or reactive gas flow, and vacuum tubular furnaces can remove air entirely for handling sensitive materials or conducting experiments in controlled environments.
Zone Control
- Single-zone furnaces maintain uniform temperature across a specific heating zone.
- Multi-zone designs (2 or 3 zones) can create temperature gradients or uniformly heat longer tubes.
Common Applications of Tubular Furnaces
Tubular furnaces are used in a wide range of scientific and industrial applications, including:
- Materials research: Sintering powders or creating composite materials
- Nanotechnology: Growing carbon nanotubes via CVD
- Metallurgy: Annealing metals and alloys
- Semiconductors: Thin-film deposition and diffusion processes
- Environmental studies: Pyrolysis and combustion analysis
How Does a Tubular Furnace Work?
- Heating Element
Electrically powered, the heating element (often wrapped around ceramic insulation) raises the temperature of the surrounding tube. - Tube Material
Samples are placed inside a quartz, alumina, or metal tube located at the furnace’s centre. - Temperature Controller
A programmable controller maintains temperature setpoints, ramp rates, and hold times for consistent results. - Atmosphere Control (Optional)
Gas inlets, valves, and vacuum ports regulate the internal environment as needed.
Choosing the Right Tubular Furnace
When selecting the right tubular furnace, consider the following key factors:
1. Maximum Temperature Requirements
- Determine the highest temperature needed for your processes.
- This will influence the choice of heating elements (e.g., Kanthal, MoSi₂) and insulation materials.
2. Tube Size and Material
- Choose a tube that suits your sample size and chemical compatibility.
- Quartz, alumina, and different types of metals are frequently used as tube materials.
3. Orientation
- A horizontal tubular furnace is well-suited for processing extended samples and supporting continuous operations.
- Vertical tubular furnace: Better for gravity-assisted reactions or precise vertical alignment.
4. Atmosphere Control
- Decide if you need to operate in air, inert gas, or vacuum conditions.
- Vacuum tubular furnaces are crucial when working with reactive or delicate materials.
5. Heating Zones
- Single-zone furnaces offer uniform heating in one section.
- Multi-zone furnaces (2–3 zones) provide better control for gradients or larger tubes.
6. Control System
- Look for advanced control features such as PID controllers or touchscreen interfaces for better precision and usability.
7. Tubular Furnace Price
- Consider your budget and compare features.
- Prices vary based on temperature range, size, zone control, vacuum capability, and automation.
- It’s important to evaluate the tubular furnace price when choosing the right model, as it can vary significantly depending on specifications and features.
Advantages of Using a Tubular Furnace
Tubular furnaces offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in both research and industrial environments:
- Compact design and cylindrical geometry provide excellent temperature uniformity and thermal efficiency.
- Customizable for a wide range of applications, including continuous flow processing and atmosphere-sensitive experiments.
- Atmosphere control via inert gases or vacuum makes them ideal for reactive materials.
- Programmable controllers enable precise control over ramp rates, dwell times, and overall temperature profiles.
Whether you’re conducting advanced materials synthesis, thermal treatments, or CVD experiments, a tubular furnace offers unmatched flexibility, consistency, and reliability.
Tubular furnaces play a vital role in laboratory and industrial environments where accurate, consistent high-temperature heating is needed. Whether conducting basic material testing or complex nanotechnology research, knowing the specific setup—such as horizontal, vertical, or vacuum tubular furnaces—is essential.
If you’re planning to invest in a high temperature tubular furnace, be sure to evaluate the specifications, construction quality, and long-term support. Don’t forget to compare features and tubular furnace prices across different manufacturers to find the best balance between performance and value. The right furnace will deliver years of reliable, high-performance results.
